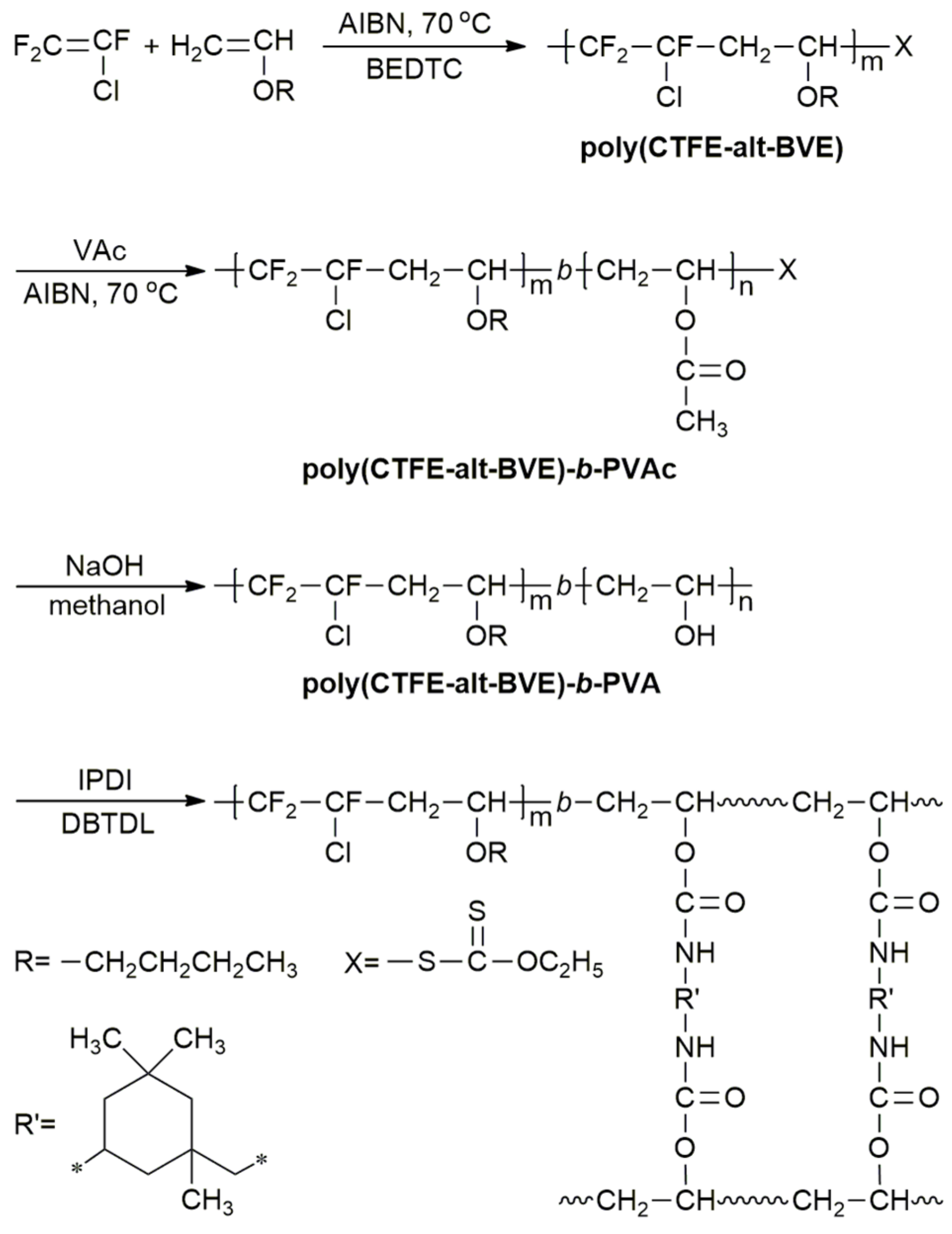
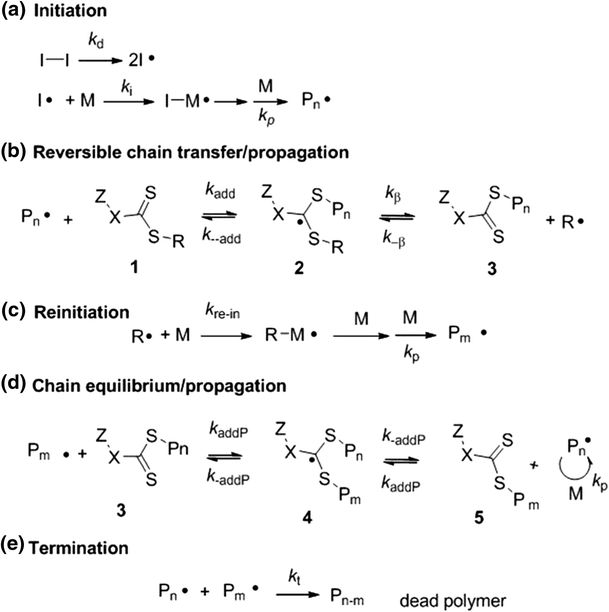
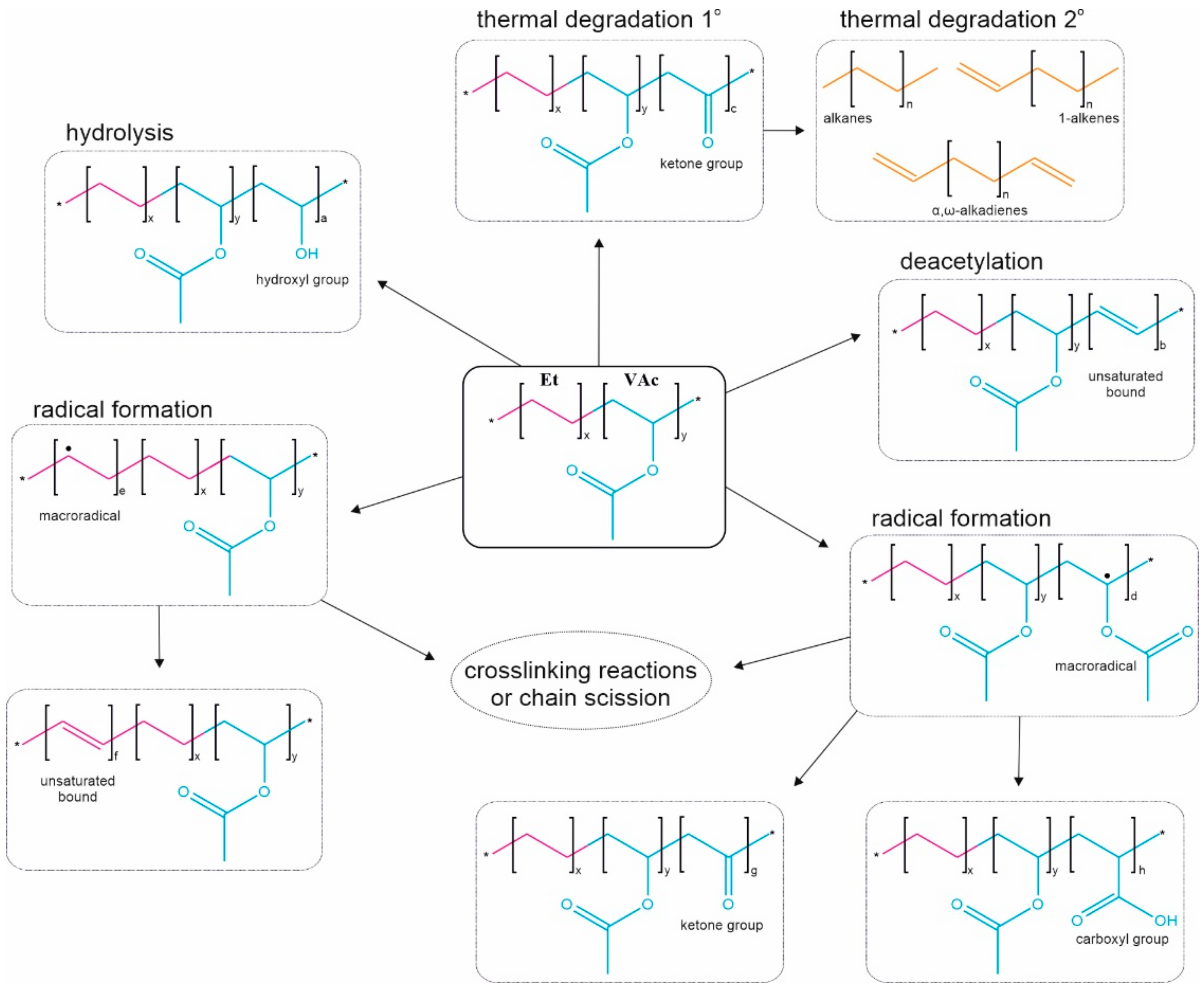
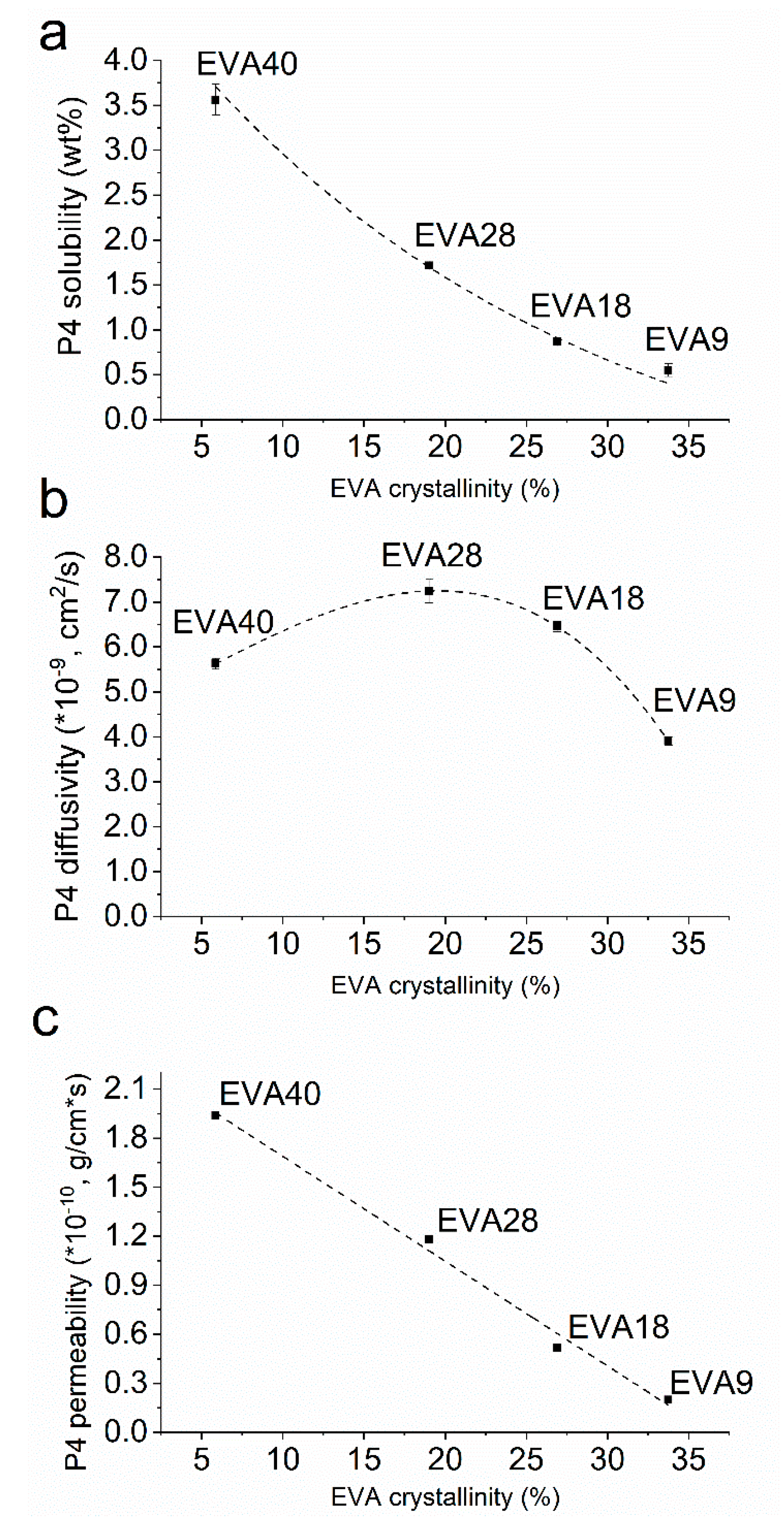
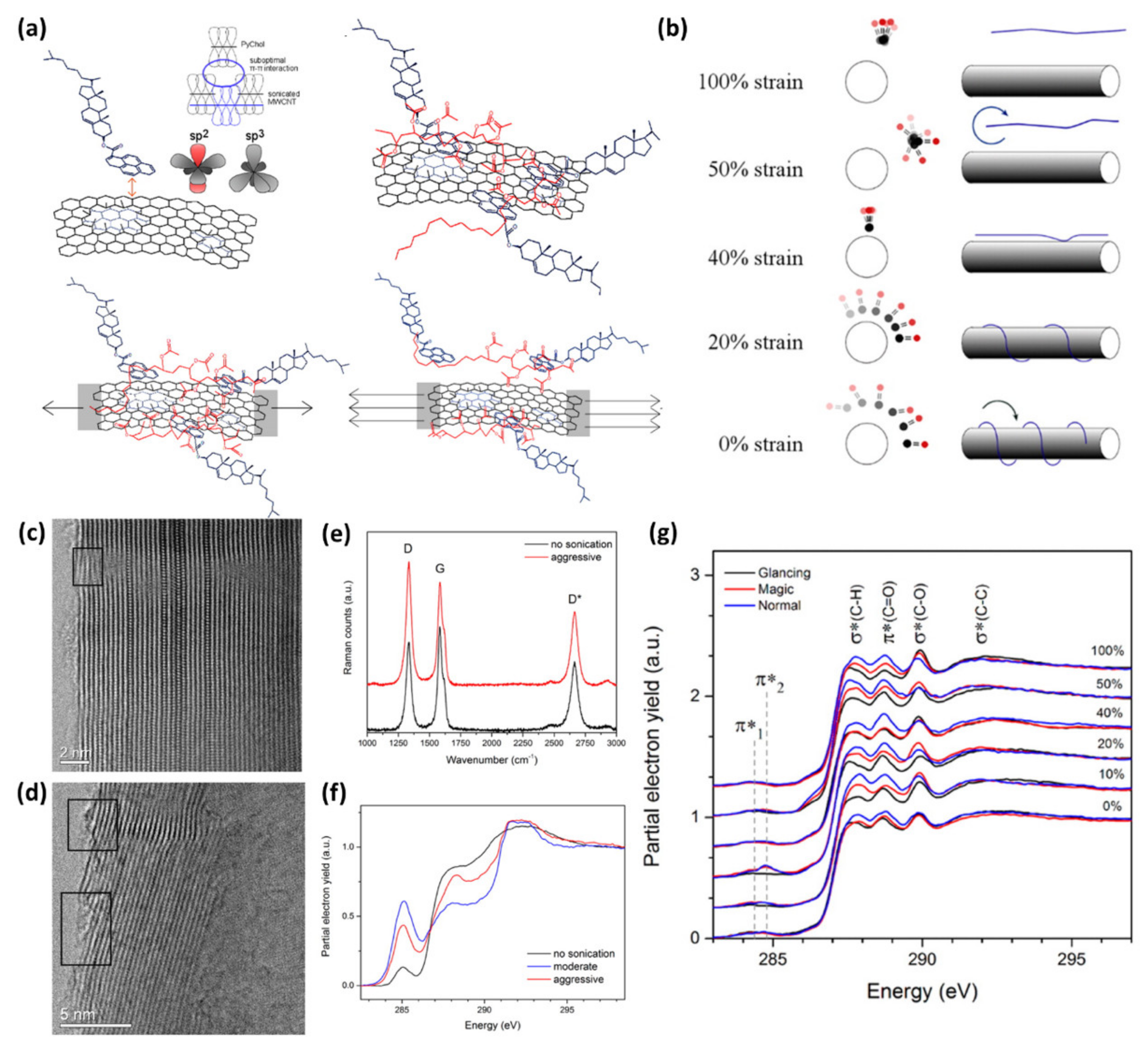
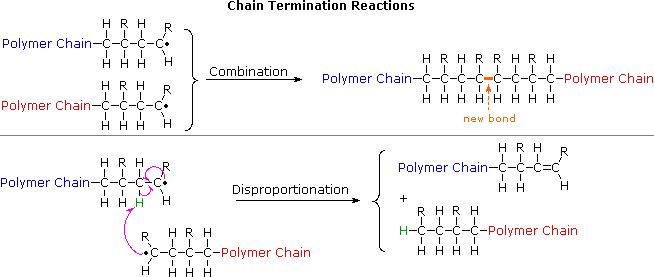
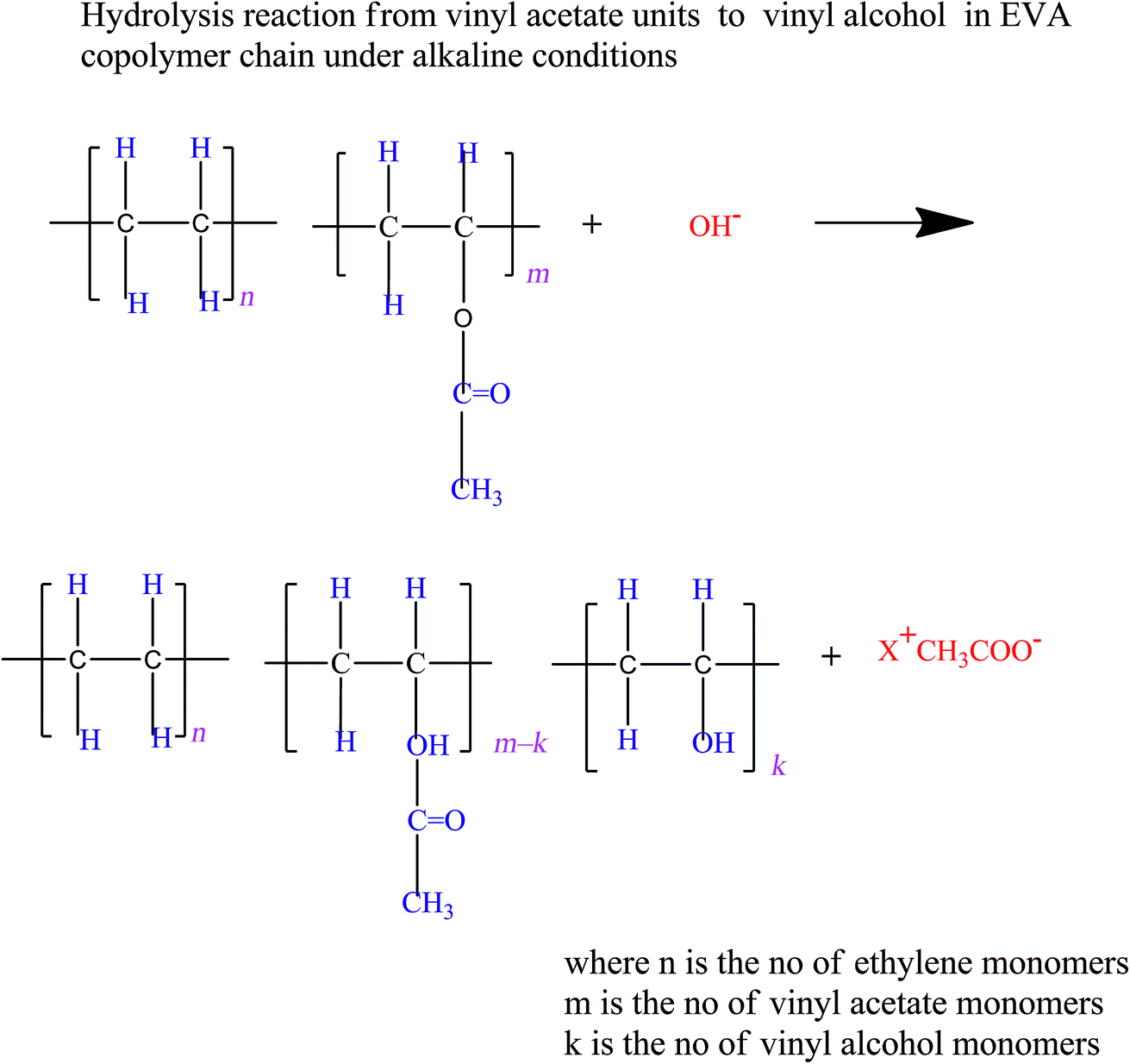
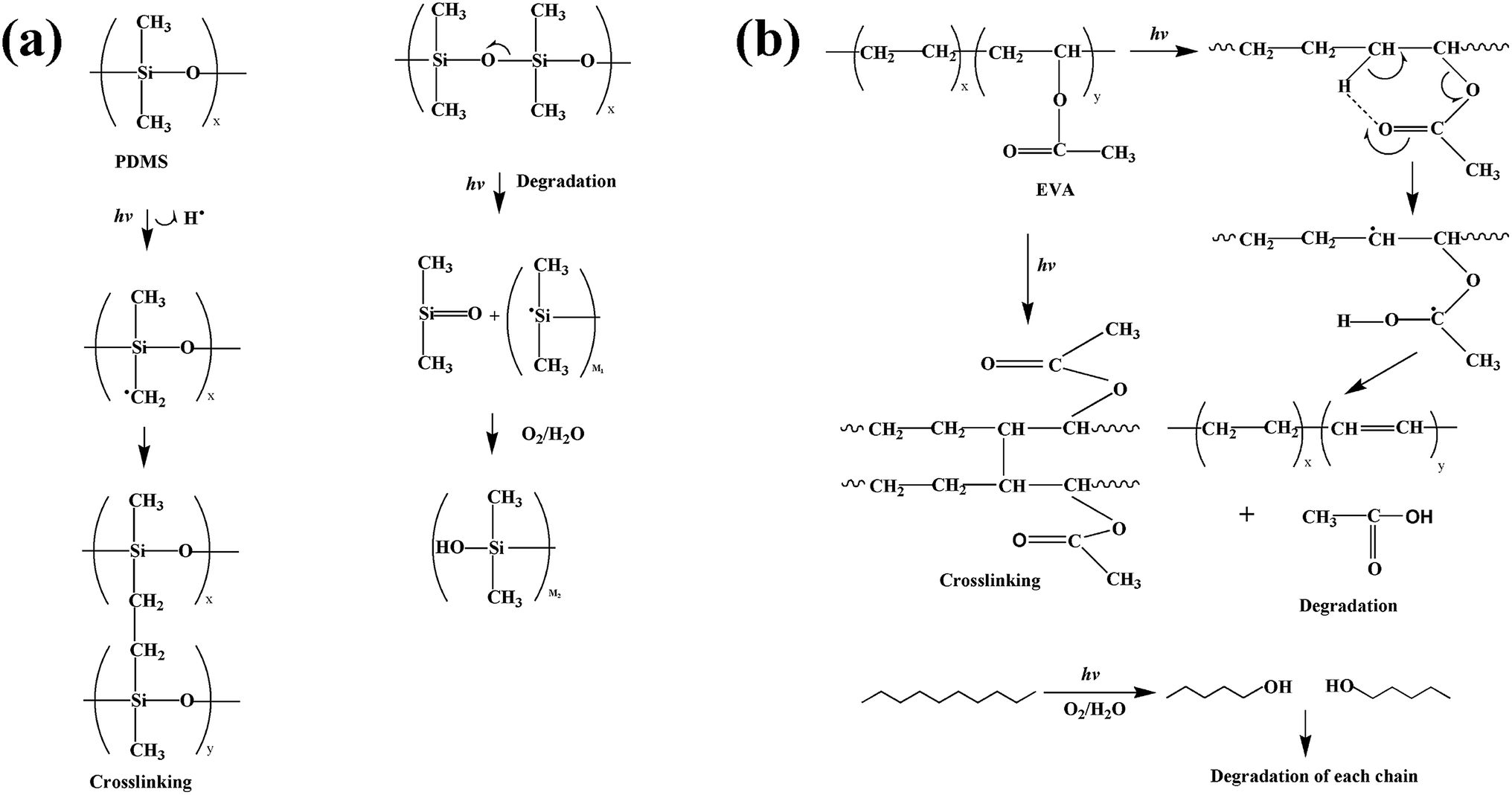
Ethylene Vinyl Acetate Polymerization Mechanism

In the production of ethylene vinyl acetate copolymers in a free radical catalyst initiated high pressure process explosive decomposition is prevented by contacting the reactor effluent downstream.
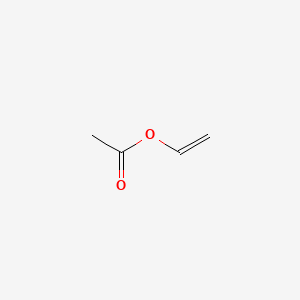
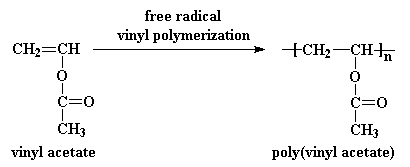
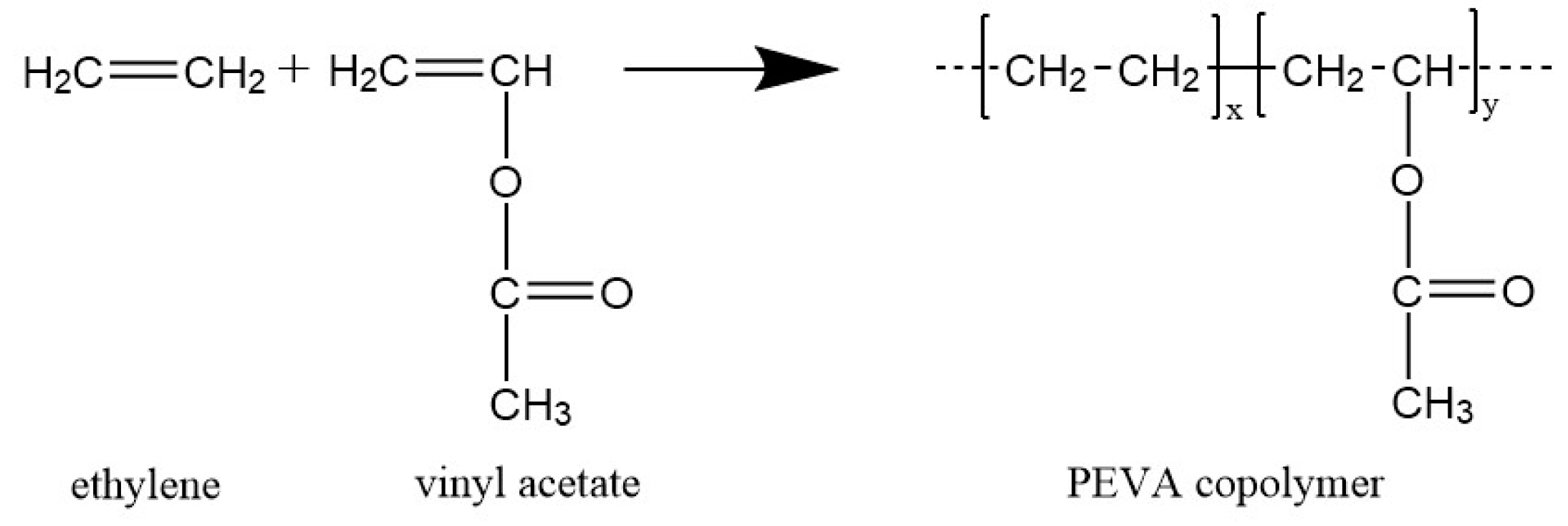
Ethylene vinyl acetate polymerization mechanism. Eva generally contains 1 50 of the va comonomer along the carbon chain backbone. The polymerization reaction is initiated by forming alkene metal complex. Eva copolymers are commercially used predominantly in the areas of coating laminating and in the film industries. Ethylene vinyl acetate eva also known as poly ethylene vinyl acetate peva is the copolymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate the weight percent of vinyl acetate usually varies from 10 to 40 with the remainder being ethylene.
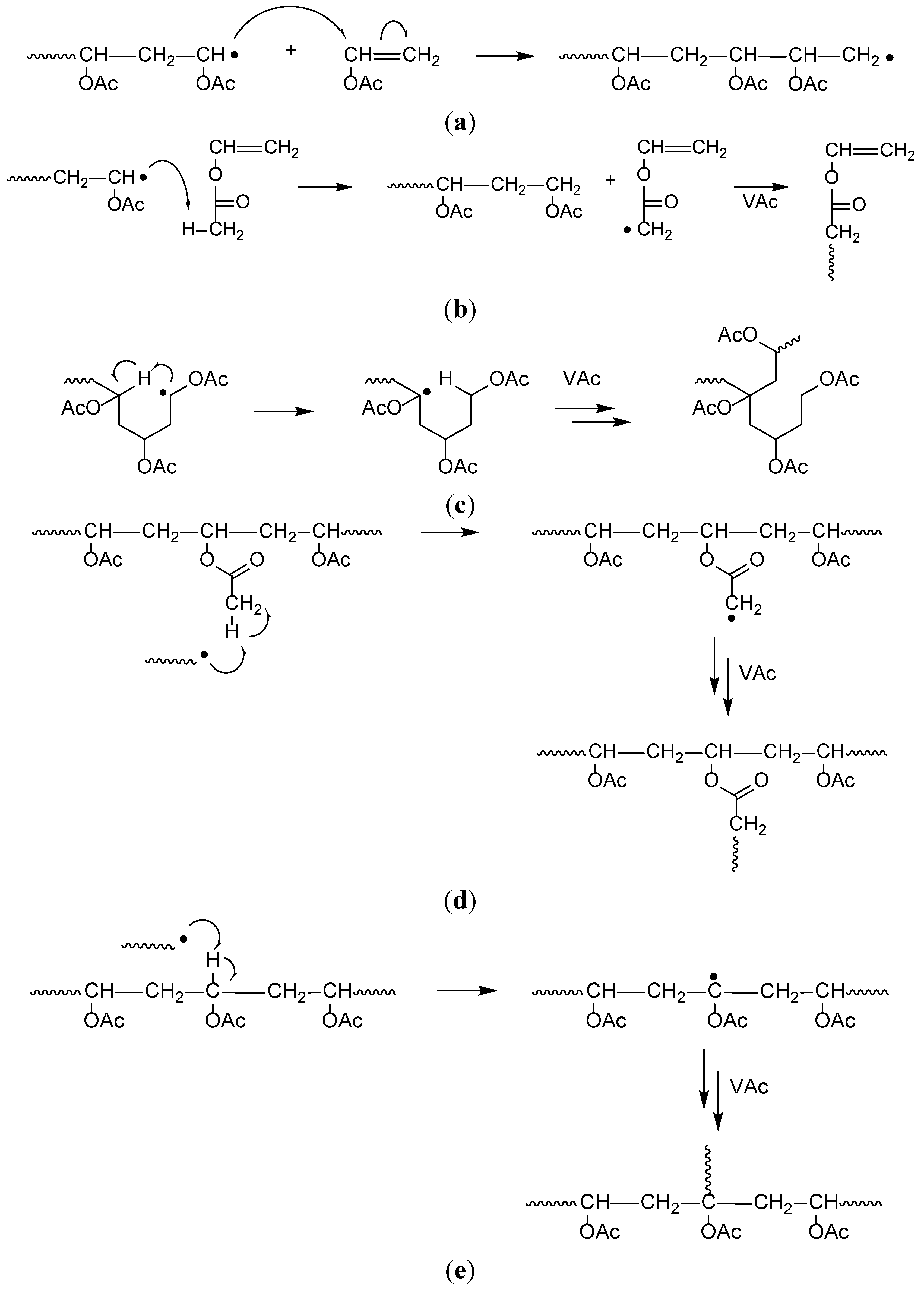
The effects of temperature pressure added co solvent vinyl acetate feed rate and emulsifier type and concentration on the rate of polymerization cumulative copolymer composition molecular. The polymerization of vinyl acetate is probably the second most frequent cause of runaway reaction accidents in the chemical industry after the phenol formaldehyde runaway reaction. By fine tuning the ethylene pressure and the vinyl acetate content a broad range of copolymers containing from 0 to 85 mol of vac unit was achieved. Therefore vinyl acetate runaway polymerization incidents are very serious and they occur with a high frequency.
12 8 1 ethylene vinyl acetate eva is a copolymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate va segments typically formed via free radical polymerization. The copolymerization by itp itcop of ethylene with vinyl acetate vac to form poly ethylene co vinyl acetate eva copolymer was also successful. Us2703794a us245079a us24507951a us2703794a us 2703794 a us2703794 a us 2703794a us 245079 a us245079 a us 245079a us 24507951 a us24507951 a us 24507951a us 2703794 a us2703794 a us 2703794a authority us united states prior art keywords ethylene vinyl acetate weight copolymer water prior art date 1951 09 04 legal status the legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. There are three different types of eva copolymer which differ in the vinyl acetate va content and the way the materials are used.
A prior extensive experimental phase identified those variables that are most important for ethylene vinyl acetate emulsion copolymer production. Coordination copolymerization of vinyl acetate vac with ethylene leading to linear copolymers that possess in chain ch 2 ch oac units has been accomplished using novel palladium complexes bearing alkylphosphine sulfonate ligands. Vinyl acetate was once prepared by hydroesterification.








.jpg)